Définition de la Jeune Entreprise Innovante
La JEI est une qualification accordée aux PME qui réalisent des opérations de recherche et développement et respectent des critères d’âge, d’indépendance et de dépenses en R&D.
Le statut permet notamment de bénéficier — sous conditions — d’exonérations d’impôt et d’exonérations de cotisations sociales pour le personnel de R&D. Ces règles ont été mises à jour ces dernières années, il faut donc se référer aux textes et fiches officielles pour les cas concrets.
What is a Young Innovative Company (JEI)?
Les entreprises travaillant sur des projets de recherche et développement peuvent prétendre au régime de la jeune entreprise innovante (JEI). Ce statut implique une réduction de la fiscalité et des charges sociales patronales pour les emplois dédiés à la recherche.
Le statut de jeune entreprise innovante a été créé en 2004 dans la perspective d’encourager la création de petites et moyennes entreprises réalisant des travaux de recherche et développement.
Ce statut a pour objectif de soutenir durablement la croissance économique en récompensant les efforts des petites et moyennes entreprises soutenant le dynamisme des activités de recherche et développement dans leur secteur d’activité.
Bon à savoir : Le dispositif JEI est véritablement incitatif en offrant d’importants avantages aux petites et moyennes entreprises, et particulièrement face à l’ouverture des marchés et l’accroissement de la concurrence à l’échelle mondiale.
Ce statut JEI offre un régime fiscal et social à part, permettant de :
- réduire la fiscalité (impôt sur les sociétés, contribution économique territoriale, taxe foncière),
- alléger le coût du travail en exonérant les cotisations sociales sur les salaires des personnels de recherche.
L’objectif du statut JEI est de donner aux PME une chance réelle de rivaliser avec les grandes structures, en leur permettant d’investir massivement dans l’innovation sans étouffer sous les charges. Cela permet en effet de ne pas laisser le monopole de l’innovation aux grands groupes, dont les moyens financiers et technologiques sont plus importants.
Le statut JEI reste l’un des dispositifs phares de soutien aux entreprises innovantes en France.
Quelques chiffres clés du JEI
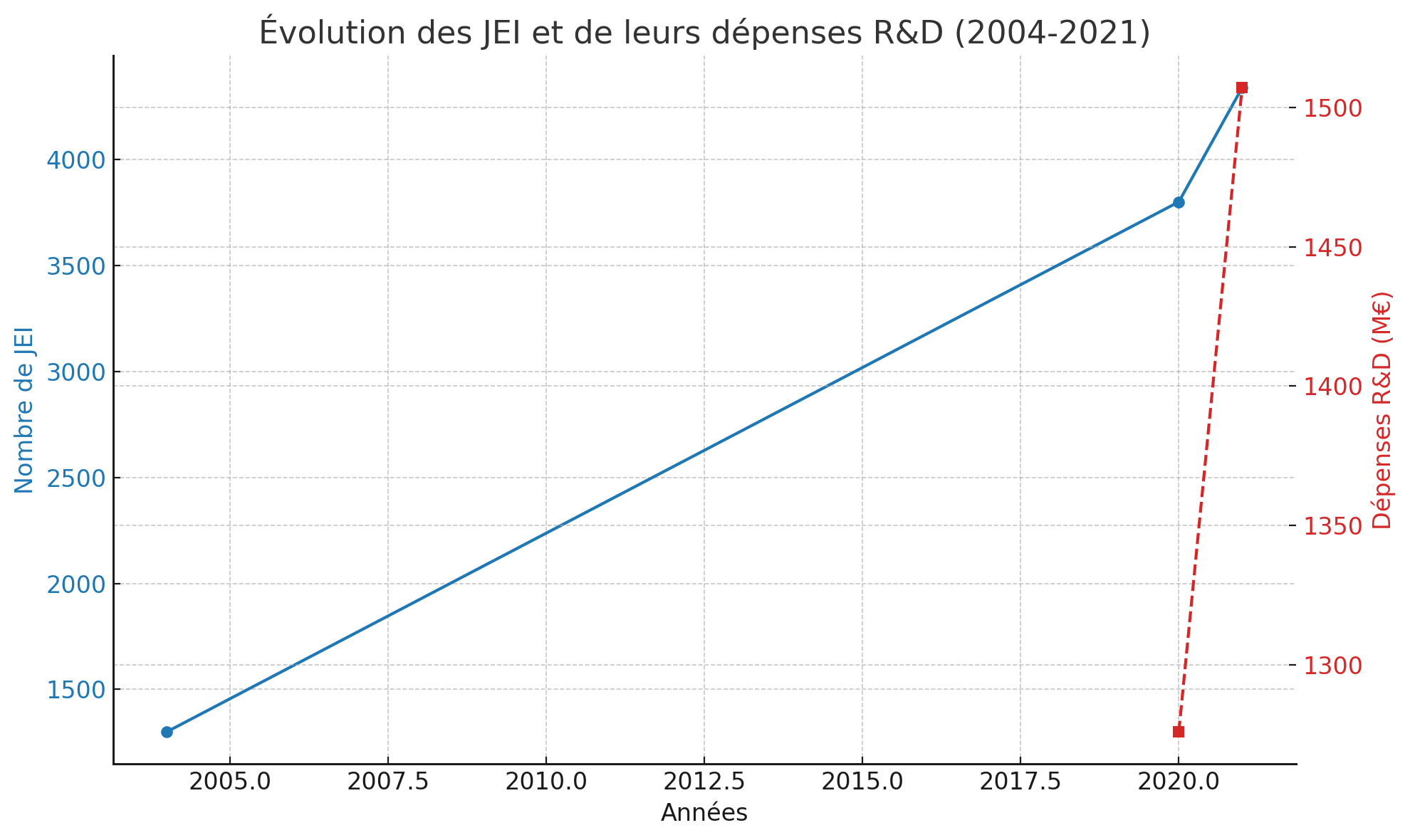
Le bilan 2021 offre un aperçu frappant de l’ampleur et de l’impact du dispositif Jeune Entreprise Innovante (JEI) en France :
- Lors de son lancement en 2004, le programme ne concernait qu’environ 1 300 bénéficiaires — un chiffre modeste, qui reflétait alors des débuts prudents.
- En 2021, ce nombre avait grimpé à 4 338 entreprises bénéficiaires, et les exonérations fiscales et sociales s’élevaient à 248 millions d’euros — soit une progression de 14 % en volume par rapport à l’année précédente (2020).
- Ces mêmes petites et moyennes entreprises ont injecté 1,507 milliard d’euros dans leurs dépenses intérieures de R&D, soit près de a 20 % de plus qu’en 2020 (1,276 milliard).
- Sur le volet des ressources humaines, ces structures rassemblaient 20 600 salariés en équivalent temps plein dédiés à la R&D.
- À titre de comparaison, les dépenses de R&D des entreprises privées en France (toutes tailles confondues) représentaient 58,9 milliards d’euros en 2022, mobilisant plus de 500 000 ETP — ce qui donne un sens concret à la contribution relative des JEI à l’écosystème national.
Ces chiffres sont révélateurs : le dispositif JEI s’est affirmé comme un pilier concret du soutien à l’innovation, avec un double impact — financier et humain. Il alimente davantage que jamais la dynamique technologique des petites et moyennes entreprises dans l’écosystème français.
Pour bénéficier du statut, l’entreprise doit être créée avant le 31 décembre 2025 et remplir plusieurs conditions :
- être jeune : avoir moins de 8 ans d’existence (11 ans si l’entreprise fut créée avant 2023) ;
- être une PME donc employer moins de 250 personnes, et réaliser un chiffre d’affaires inférieur à 50 M€ ou un total de bilan inférieur à 43 M€ ;
- être indépendante : au moins 50 % du capital détenu par des personnes physiques, d’autres JEI, des associations reconnues d’utilité publique ou des organismes de recherche ;
- être innovante : consacrer au moins 15 % des charges fiscalement déductibles à la R&D ;
- ne pas être issue d’une restructuration : ne pas résulter d’une concentration, d’une reprise ou d’une extension d’activité préexistante.
À noter : les dépenses d’innovation (au sens large) ou de veille technologique ne sont pas éligibles. Seules les dépenses de R&D au sens strict sont prises en compte .
Dépenses de R&D prises en compte
Les dépenses éligibles sont encadrées par le Code général des impôts. On retrouve notamment :
- les dotations aux amortissements d’immobilisations dédiées à la recherche (prototypes, installations pilotes) ;
- les salaires et charges sociales des chercheurs, techniciens et personnels directement affectés à la R&D ;
- Les primes et rémunérations supplémentaires des salariés auteurs d’inventions brevetées ;
- les frais de sous-traitance confiés à des organismes publics, associations reconnues d’utilité publique ou établissements d’enseignement supérieur ;
- les dépenses liées aux brevets et certificats d’obtention végétale (prise, défense, maintenance).
Quelles conditions pour obtenir le statut JEI ?
Le statut est délivré par l’administration fiscale. Si vous souhaitez bénéficier du statut de Jeune Entreprise, vous devez adresser à votre Service des Impôts des Entreprises (SIE) le formulaire officiel .
Le SIE dispose de 4 mois pour notifier son avis, opposable à l’URSSAF.
Prenons un exemple de calcul simplifié pour vérifier l'éligibilité d’une entreprise au statut JEI. Supposons une PME qui dépense 200 k€ sur l’exercice, dont :
- salaires R&D 120 k€,
- amortissements 30 k€,
- sous-traitance 50 k€.
Les dépenses R&D représentent 60 % des charges : bien au-delà du seuil de 15 %.
Si l’entreprise remplit les autres critères d’âge et d’indépendance, elle peut demander le statut JEI : l’exonération sociale sur la fraction des salaires R&D sera calculée selon les règles URSSAF, et l’exonération fiscale s’appliquera seulement si la date de création la rend éligible à l’IS (voir restriction 2024).
Cet exemple est indicatif, un expert-comptable doit bien entendu valider les montants et les écritures.
Les démarches à effectuer pour être JEI
-
Constituer le dossier : description technique du projet R&D, tableaux des dépenses prévues et réalisées, preuves d’indépendance capitalistique, et les comptes.
-
Formulaire / demande d’avis : envoyer le modèle de demande d’avis aux services fiscaux (Service des Impôts des Entreprises – SIE). Le modèle et la notice sont disponibles sur Service-Public.
-
Instruction : l’administration dispose d’un délai (classiquement 4 mois) pour rendre un avis. Cet avis est opposable à l’URSSAF pour obtenir les exonérations sociales.
Voici une check-list pratique pour constituer le dossier JEI, contenant les différents éléments à réunir pour faire vos démarches et obtenir le statut de Jeune Entreprise Innovante (JEI) :
- Fiche projet R&D : objectifs, méthodologie, calendrier.
- Tableaux financiers : dépenses R&D détaillées (salaires, amortissements, sous-traitance).
- Justificatifs RH : fiches de poste, temps passé en R&D, bulletins de salaire.
- Statuts et répartition du capital (preuve d’indépendance).
- Formulaire de demande d’avis / modèle CERFA (Service-Public).
N’hésitez pas à vous faire aider d’un expert-comptable.
Avantages fiscaux et sociaux du statut JEI
Le statut JEI est attractif car il combine allégements fiscaux et exonérations sociales.
Avantages fiscaux du statut JEI
Exonération d’Impôt sur les sociétés (IS) :
L’exonération est totale pendant le premier exercice bénéficiaire, puis l’exonération se fait à hauteur de 50 % sur l’exercice suivant. Toutefois, depuis la loi de finances 2024, les entreprises créées à partir du 1er janvier 2024 ne bénéficient plus de l’exonération d’IS (source officielle).
Exonération de cotisation foncière des entreprises (CFE) :
L’exonération de Contribution Économique Territoriale est possible pendant 7 ans, sur délibération des collectivités locales. LA CET inclut à l’origine deux taxes : la Cotisation Foncière des Entreprises (service-public.fr) et la CVAE (supprimée progressivement depuis 2024).
Exonération de cotisation foncière sur les propriétés bâties (TFPB) :
L’exonération de taxe foncière dure jusqu’à 7 ans, sur décision de la commune.
Avantages sociaux du statut JEI : exonération de cotisations sociales
Les JEI peuvent exonérer les cotisations patronales sur les salaires des personnels de R&D, à savoir :
- chercheurs et techniciens ;
- lawyers in charge of industrial protection ;
- personnels effectuant des tests pré-concurrentiels ;
- chefs de projet en R&D.
Cette exonération s’applique :
- sur les cotisations maladie, maternité, invalidité-décès, vieillesse et allocations familiales ;
- jusqu’à 4,5 fois le SMIC par salarié ;
- pendant maximum 8 ans (vous pourrez en savoir plus sur urssaf.fr).
Par exemple, en 2025, l’exonération cesse au-delà d’un salaire mensuel brut de 7 213 € environ.

Plafonds et règles européennes : aides « de minimis »
Les exonérations publiques sont encadrées par la réglementation européenne sur les aides « de minimis ».
Depuis le nouveau règlement européen entré en vigueur, le plafond général a été relevé à 300 000 € sur 3 exercices fiscaux glissants (règle applicable pour la période récente), avec des exceptions sectorielles. Il est donc essentiel, lors d’une demande de statut JEI, de déclarer les aides déjà perçues.
Tableau récapitulatif des conditions et avantages JEI
|
Critères / Avantages
|
Détails
|
|
Âge de l’entreprise
|
< 8 ans (11 ans si créée avant 2023)
|
|
Taille
|
< 250 salariés, CA < 50 M€ ou bilan < 43 M€
|
|
Indépendance
|
≥ 50 % du capital détenu par des personnes physiques/JEI/associations reconnues
|
|
Dépenses R&D
|
≥ 15 % des charges fiscalement déductibles
|
|
Impôt sur les sociétés (IS)
|
Exonération totale 1 an + 50 % l’année suivante (supprimé pour entreprises créées après 01/01/2024)
|
|
CET / TFPB
|
Exonération possible jusqu’à 7 ans (décision locale)
|
|
Exonérations sociales
|
Salaires R&D, jusqu’à 4,5 SMIC, max 8 ans
|
|
Plafond aides publiques
|
300 000 € sur 3 exercices consécutifs
|
JEI et JEU : une déclinaison universitaire
En parallèle du statut JEI, il existe le statut de Jeune Entreprise Universitaire (JEU).
Il s’adresse aux sociétés créées par des étudiants, enseignants ou chercheurs et repose sur la valorisation des travaux de recherche issus d’établissements d’enseignement supérieur (détails sur Bpifrance).
Points de vigilance et bonnes pratiques
Pour tirer pleinement parti du statut de Jeune Entreprise Innovante tout en évitant les mauvaises surprises, certaines précautions s’imposent.
D’abord, il est essentiel de documenter minutieusement toutes les dépenses de R&D. Chaque facture, chaque contrat de sous-traitance, chaque amortissement doit pouvoir être rattaché clairement à un projet de recherche. En cas de contrôle, l’administration exigera des pièces justificatives solides pour valider l’éligibilité des dépenses déclarées.
Il est également recommandé d’anticiper un éventuel audit en préparant dès le départ des fiches de poste détaillées pour les salariés impliqués, ainsi que des feuilles de temps précisant leur part de travail dédiée à la recherche. Cette traçabilité interne permet non seulement de rassurer l’administration, mais aussi de gagner en crédibilité auprès d’éventuels investisseurs.
Autre point crucial : le cumul avec d’autres dispositifs d’aide. Les exonérations liées au statut JEI entrent dans le cadre des aides dites « de minimis ». Il faut donc recenser toutes les subventions ou soutiens déjà perçus et vérifier que leur montant cumulé ne dépasse pas le plafond actuel de 300 000 € sur trois exercices fiscaux glissants.
Enfin, il convient de rester attentif aux évolutions de la réglementation. La jurisprudence et les mises à jour du BOFiP peuvent modifier l’interprétation de certaines règles, notamment pour les entreprises créées après 2024, dont les exonérations fiscales ont été partiellement supprimées.
Suivre ces évolutions régulièrement est indispensable pour sécuriser sa stratégie et adapter son organisation.





 Menu / Adresses
Menu / Adresses Menu / Fiches pratiques
Menu / Fiches pratiques Menu / Services
Menu / Services




 Menu / Adresses
Menu / Adresses Menu / Fiches pratiques
Menu / Fiches pratiques Menu / Services
Menu / Services







